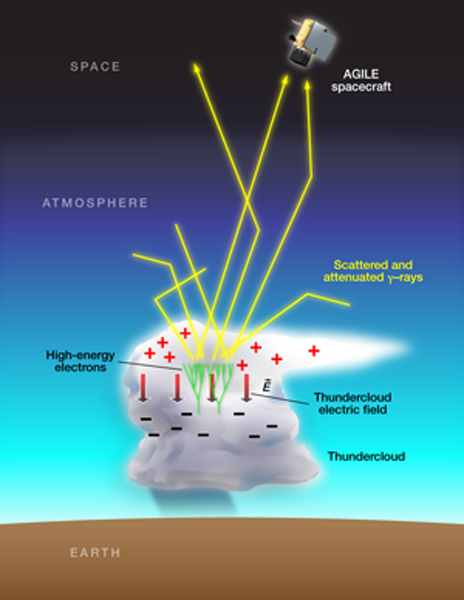
The AGILE satellite detects “super-energetic TGFs” that could affect air travel. “Terrestrial Gamma-Ray Flashes” (TGF) are phenomena of terrestrial (atmospheric) origin only lasting a few milliseconds that are likely associated to very intense tropical thunderstorms. The AGILE satellite detected several of these events since its first months of operations. The AGILE equatorial orbit, together with its advanced payload capabilities, allowed the discovery of TGFs with gamma-ray energy reaching up to 50 MeV. Such highly energetic radiation must be produced in atmospheric conditions requiring potential differences of 100 Mega Volts or more, hundreds of times larger than that required to produce the usual terrestrial lightning. As announced in a joint press release that can be found on the ASI and INAF websites, the AGILE Team and ASI are collaborating with ENAC (Ente Nazionale per l’Aviazione Civile) to understand the possible hazards to air traffic that these very energetic atmospheric events might cause. THE AGILE Team reported the detection of TGFs up to 40 MeV in the paper by Marisaldi et al., JGR, 115, A00E13, 2010.
The AGILE satellite detects “super-energetic TGFs”
Leave a reply